Photosynthesis in plants is one of the most essential biological processes that sustain life on Earth. It is the means by which green plants, algae, and certain bacteria convert sunlight into chemical energy. This natural process not only provides food for plants themselves but also supports all life forms by producing oxygen and forming the base of the food chain.
In this article, we’ll explore what is photosynthesis in plants, understand its definition, delve into the photosynthesis process, and break down the photosynthesis equation for better understanding.
What is Photosynthesis in Plants?
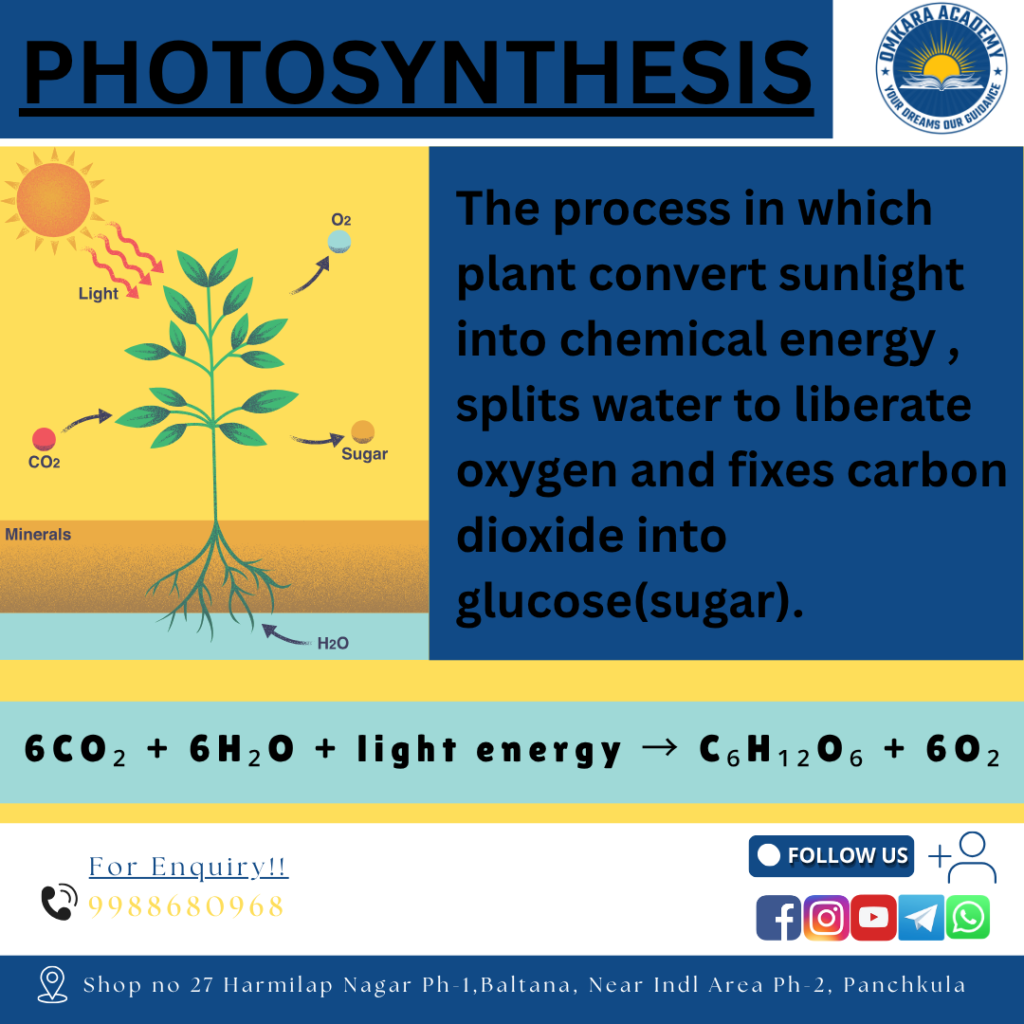
Photosynthesis in plants refers to the process by which they use sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to create glucose (a type of sugar) and release oxygen as a byproduct. This process takes place mainly in the chloroplasts of plant cells, which contain a green pigment called chlorophyll. Chlorophyll absorbs light energy, initiating the chemical reactions that drive photosynthesis.
Simply put, photosynthesis is how plants make their own food. Unlike animals, which must consume food for energy, plants are autotrophs, meaning they can produce their own nutrients through photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis Definition
The scientific definition of photosynthesis is:
“Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants and some other organisms use sunlight to synthesize nutrients from carbon dioxide and water. It generally involves the green pigment chlorophyll and generates oxygen as a byproduct.”
This definition highlights the crucial role of sunlight and chlorophyll, as well as the key outputs: glucose and oxygen.
The Photosynthesis Process
The process of photosynthesis in plants occurs in two main stages:
1. Light-Dependent Reactions (Photochemical Phase)
These reactions take place in the thylakoid membranes within chloroplasts and require direct sunlight. The main steps include:
- Absorption of light by chlorophyll.
- Splitting of water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen (a process called photolysis).
- Release of oxygen as a byproduct.
- Conversion of ADP and NADP+ into energy-rich compounds like ATP and NADPH.
2. Light-Independent Reactions (Calvin Cycle or Dark Reactions)
These occur in the stroma of the chloroplasts and do not require direct light but rely on the products of the light-dependent reactions. The steps include:
- Carbon fixation: Carbon dioxide from the atmosphere is incorporated into a stable intermediate.
- Reduction phase: ATP and NADPH help convert the fixed carbon into glucose.
- Regeneration: The cycle regenerates molecules needed for the process to continue.
Together, these two stages enable plants to convert light energy into chemical energy, store it in glucose molecules, and use it to grow and function.
Photosynthesis Equation
The overall balanced photosynthesis equation can be represented as:
6CO₂ + 6H₂O + light energy → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂
Where:
- CO₂ = Carbon Dioxide
- H₂O = Water
- C₆H₁₂O₆ = Glucose
- O₂ = Oxygen
This equation summarizes the entire process of photosynthesis in plants. It shows how six molecules of carbon dioxide and six molecules of water, in the presence of light energy, are converted into one molecule of glucose and six molecules of oxygen.
Importance of Photosynthesis in Plants
Photosynthesis is vital for several reasons:
- Food Production: Plants use the glucose produced during photosynthesis for energy and growth. Animals, in turn, rely on plants for food, either directly or indirectly.
- Oxygen Generation: Photosynthesis releases oxygen into the atmosphere, which is essential for the survival of most living organisms.
- Carbon Dioxide Reduction: It helps maintain atmospheric balance by removing carbon dioxide, a major greenhouse gas.
- Energy Transfer: It is the starting point of the food chain, allowing energy from the sun to flow through ecosystems.
- Raw Material for Plant Growth: Glucose produced in photosynthesis is converted into cellulose, starch, and other organic compounds required for plant structure and development.
Factors Affecting Photosynthesis in Plants
Several environmental factors influence the rate of photosynthesis:
- Light intensity: More light increases the rate up to a point.
- Carbon dioxide concentration: Higher CO₂ levels can enhance the rate.
- Temperature: Optimal temperatures promote enzyme activity involved in the process.
- Water availability: Water stress can limit photosynthesis by causing stomatal closure.
Understanding these factors helps in improving crop yields and managing ecosystems.
Conclusion
Photosynthesis in plants is not just a biological process; it’s the foundation of life on Earth. From food production to oxygen release, it supports every living being in some way. By understanding the photosynthesis definition, process & equation, we gain a deeper appreciation for the green plants around us and their critical role in sustaining life.
Whether you’re a student, a gardener, or simply someone curious about nature, knowing what is photosynthesis in plants helps you connect more deeply with the natural world.
For more updates keep in touch with omkaraacademy.


